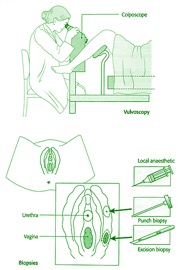
What is vulvoscopy?
A vulvoscopy is an examination of the vulval skin performed using colposcope to investigate vulval diseases and problems including precancer and cancer of the vulva. Vulvoscopy is performed if women have vulval soreness, itching, bleeding or an abnormal lump.
How is it performed?
Vulvoscopy is usually carried out in clinic and do not require general anaesthetic. After antiseptic preparations colposcope is used to to magnify vulval skin. Light attached to colposcope illuminates vulval skin and camera attached to colposcope can relays images to television screen. Acetic acid and/or Lugol’s iodine solution may be used to identify abnormal areas in vulval skin.
Small diagnostic (punch) biopsy may be carried out depending on the findings of the vulvoscopic examination. Local anaesthetic injection is used prior to taking biopsy.
How long does it take?
Vulvoscopy usually takes about 5mins but if vulval biopsy is required it can take additional 10mins.
What are the risks and complications?
Vulvoscopy is a very simple examination and does not have any major risk. If biopsy is taken, rarely, women may experience minor bleeding or infection
If your cyst is particularly large, or there’s a chance it could be cancerous, a laparotomy may be recommended. During a laparotomy, a single, larger cut is made in your tummy to give the surgeon better access to the cyst.
The whole cyst and ovary may be removed and sent to a laboratory to check whether it’s cancerous. Stitches or staples will be used to close the incision.
You may need to stay in hospital for a few days after the procedure.
What will happen after surgery?
After the ovarian cyst has been removed, you’ll feel pain in your tummy, although this should improve in a day or two. Following laparoscopic surgery, you’ll probably need to take things easy for two weeks. Recovery after a laparotomy usually takes longer, possibly around four to six weeks. If the cyst is sent off for testing, the results should come back in a few weeks and Mr Chattopadhyay will discuss with you whether you need any further treatment.
Contact Mr Chattopadhyay or your GP if you notice the following symptoms during your recovery: heavy bleeding, severe pain or swelling in your abdomen, a high temperature (fever), dark or smelly vaginal discharge. These symptoms may indicate an infection.